Cytochromes P450 are a family of enzymes that play an important role in metabolism. There are about a hundred isoenzymes, of which 7 are considered the most important: CYP 1A2, CYP 2B6, CYP 2C8, CYP 2C9, CYP 2C19, CYP 2D6 and CYP 3A4. The latter alone is responsible for the metabolism of 50% of marketed drugs.
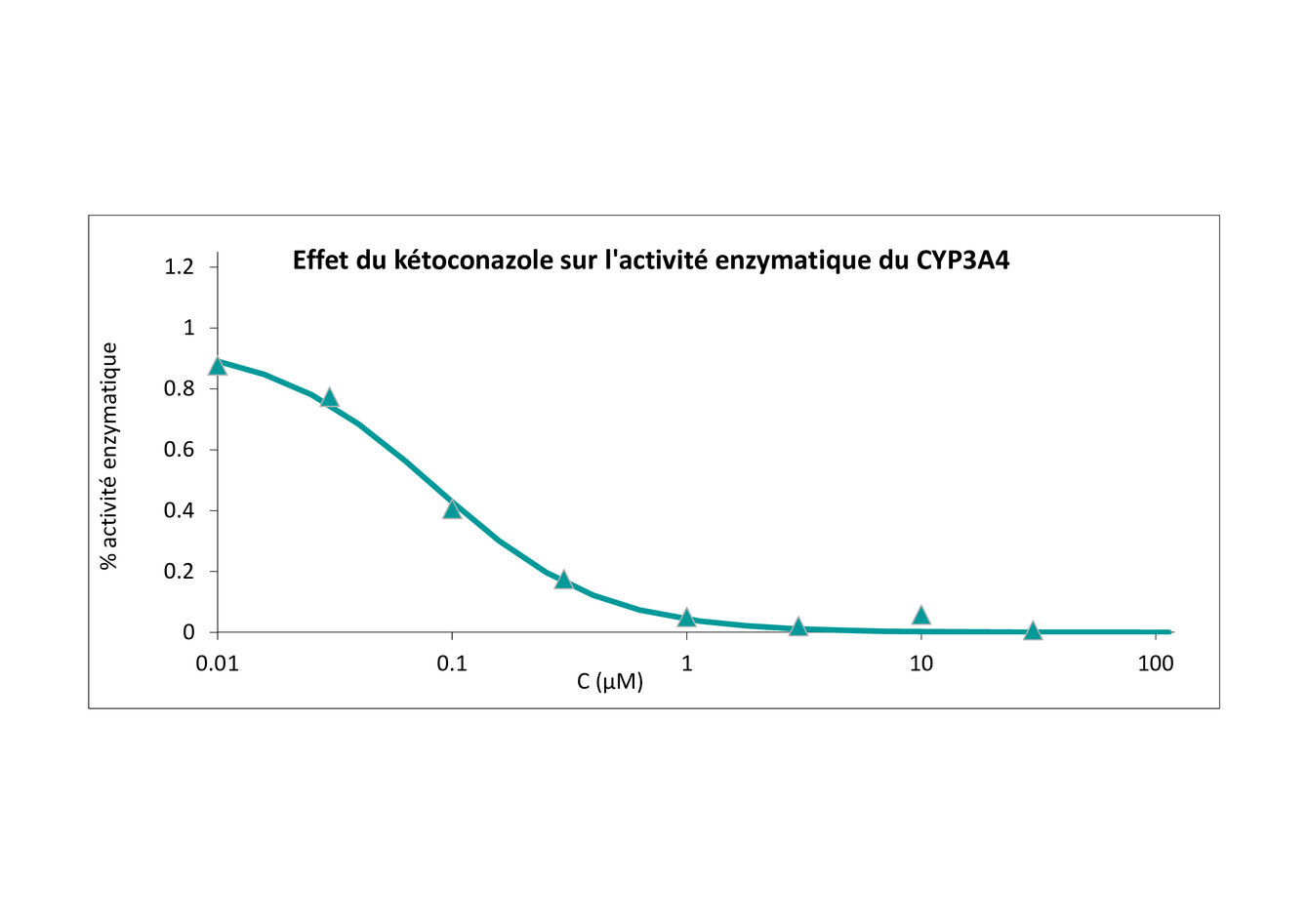
Assessing a compound's potential to inhibit CYP450 is important because of the risk of drug interaction. If more than one compound is co-administered, one may inhibit the metabolism of the other. This may affect plasma concentrations and potentially lead to adverse reactions or toxicity.