Permeability is the rate at which a compound passes through a biological barrier.
This process is involved in intestinal absorption but also in the distribution of compounds from the blood to organs like liver, brain, kidneys.
The majority of drugs enter the bloodstream by passive diffusion through the intestinal epithelium.
PAMPA (Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay) is an in vitro model of passive absorption.
Protocol
| Matrix | PBS pH 7.4 |
| Membrane | Solution of 2% phosphatidylcholine in dodecane |
| Test concentration | 10µM |
| Test temperature | Room temperature |
| Incubation time | 16h |
| Controls | Chloramphenicol, Testosterone |
| Analysis method | LC-MS/MS |
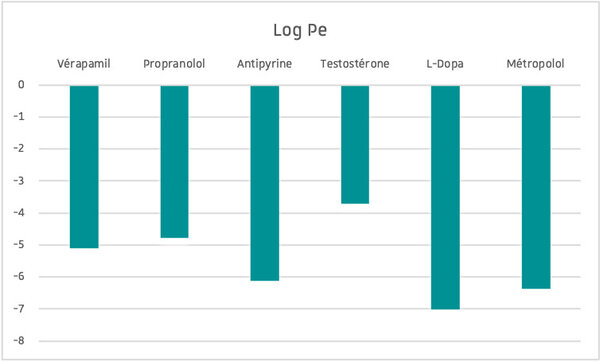
| Data delivery | Log Pe |
| Replicate | 3 |
Data
Notes
The PAMPA method can not predicts passive diffusion.
All the mechanisms involved in intestinal permeability are studied with another method: Caco-2.