The lipophilicity of a molecule influences its absorption and distribution between tissues.
The partition coefficient between octanol and water is the most widely used physicochemical parameter to measure lipophilicity. Its determination by the classic method (shake flask) takes time and is not always appropriate for the most hydrophobic molecules.
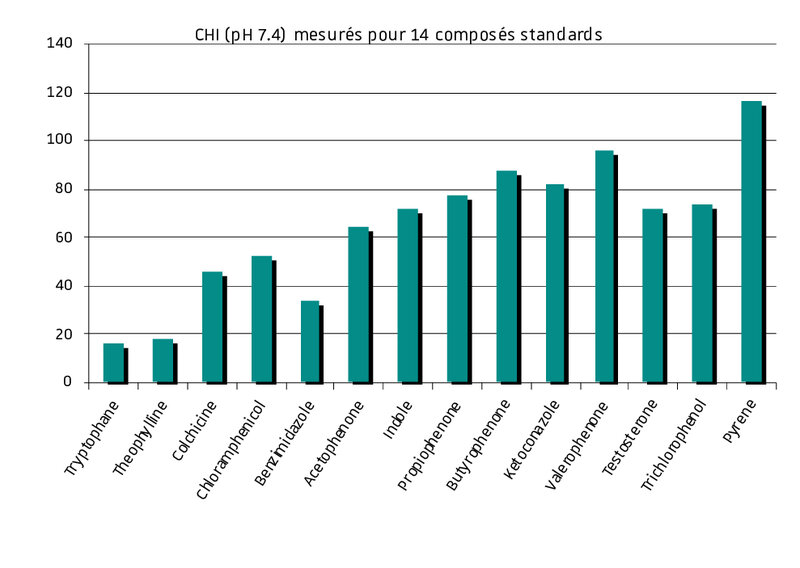
The CHI (Chromatographic Hydrophobicity Index) method is an alternative measure of lipophilicity determined by HPLC, using a rapid gradient.
This technique makes it possible to have a good estimate of lipophilicity at medium throughput and at a lower cost.