Introduction
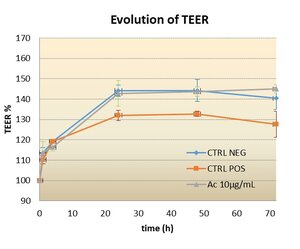
The effect of compounds on the integrity of the intestinal barrier can be assessed by measuring the change in resistance of a monolayer of Caco-2 cells after addition of the compound.
The Caco-2 cell line (derived from human colorectal carcinoma) is the model used in vitro to characterise the effects of compounds on the intestinal barrier.