Introduction
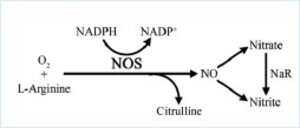
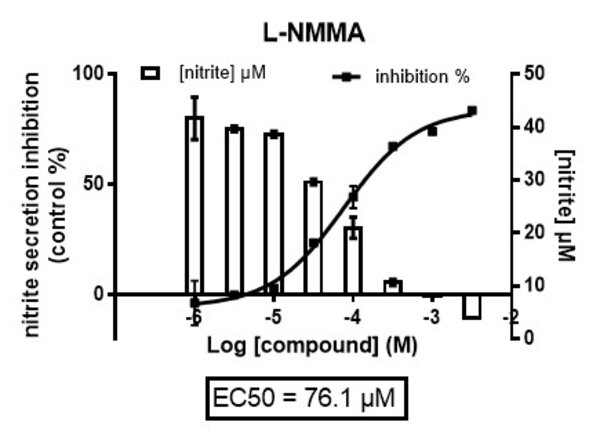
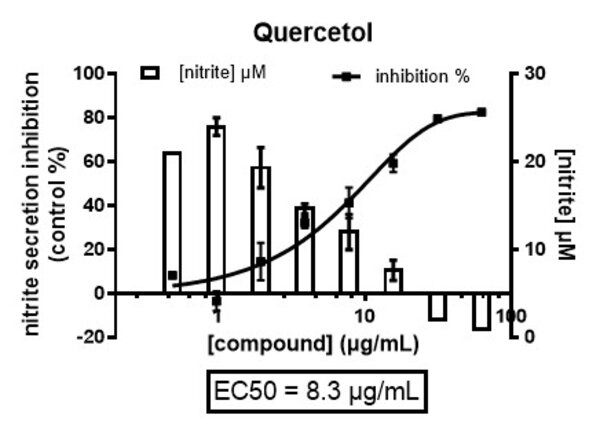
Nitric oxide (NO) plays a key role in the inflammatory response by activating several signaling pathways that exacerbate the deleterious effects of oxidative stress.
The quantification of nitric oxide (NO) is therefore a relevant biological target in the search for anti-inflammatory agents.