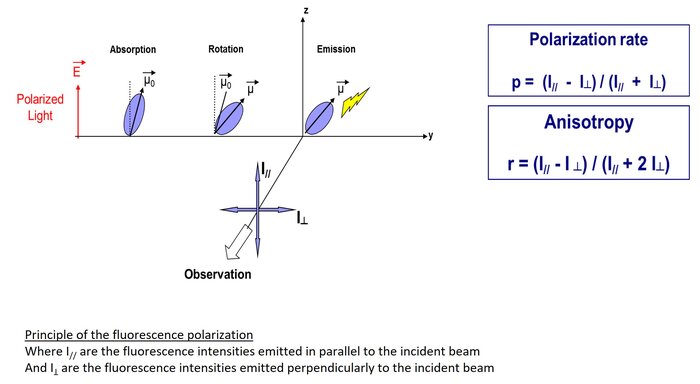
The principle of the fluorescence polarization is based on :
1- the ability of a fluorophore to be excited by polarized light
2- the ability of the fluorescent molecule to rotate during its "excited" state.
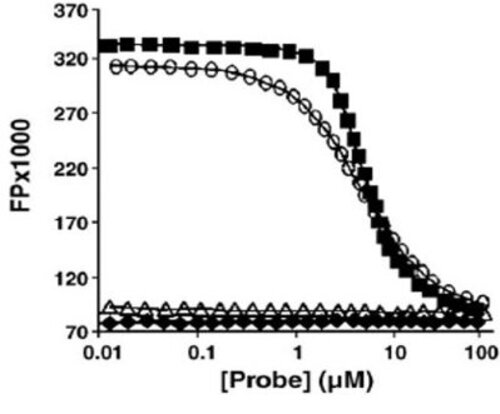
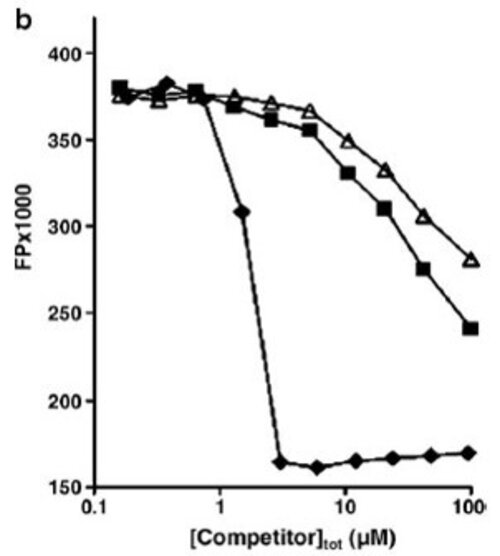
The degree of the fluorescence polarization, defined by the polarization rate (p) or by the anisotropy (r), measures the changes in orientation of the fluorescence emission after excitation of the fluorophore by a polarized light.
Thus, if a small fluorescent molecule is "free", its ability to rotate in the medium will be high, which will induce a depolarization of the fluorescence emission (= Low polarization rate). On the other hand, if it’s bound to a larger molecule such as a protein, its ability to rotate will be greatly reduced, and therefore will not change the direction of fluorescence emission (= High polarization rate).